Archives
- 2026-03
- 2026-02
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2018-07
-
br Materials and Methods br Results br
2024-09-05
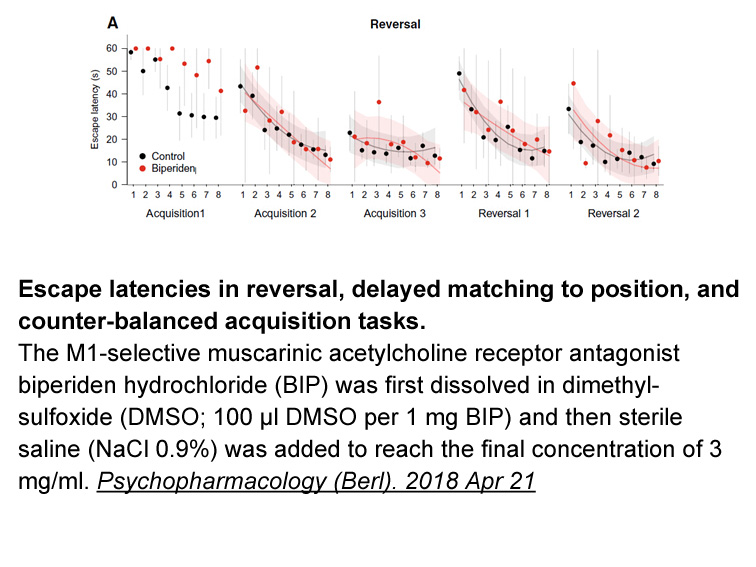
Materials and Methods Results Discussion XHP is a traditional Chinese anti-cancer medicine that is widely used for the treatment and adjuvant treatment of breast cancer. XHP has been shown to induce apoptosis in various breast cancer ha peptide in vitro, including Hs578T, MCF-7, and MDA-MB
-
br Materials and methods br
2024-09-05
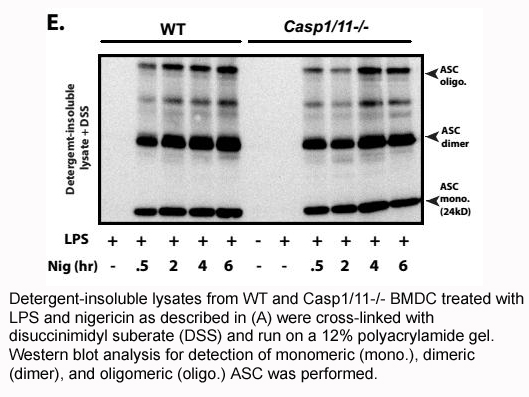
Materials and methods Results and discussion Conclusions Acknowledgements Introduction Infections in children aged 0–21 years who reside in long-term care (LTC) facilities are common due to underlying complex medical conditions, use of invasive devices such as urinary catheters and ve
-
Prostate cell growth and prostate carcinogenesis are not onl
2024-09-05
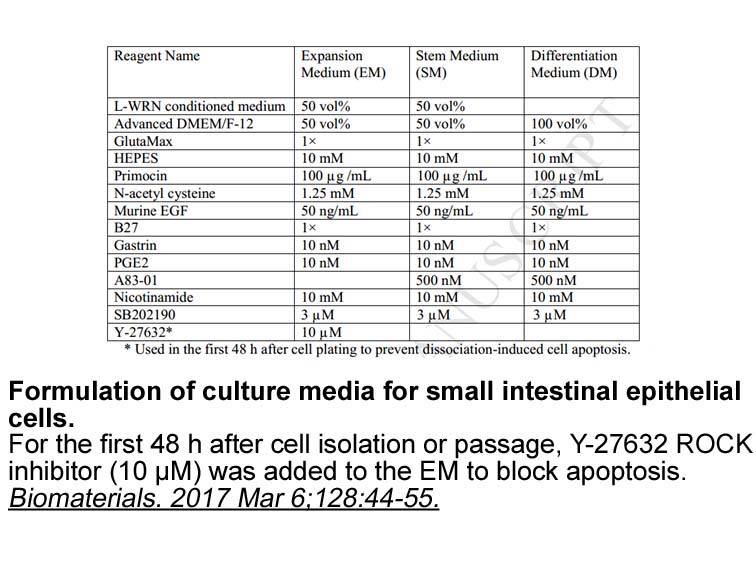
Prostate cell growth and prostate carcinogenesis are not only mediated by androgens, they are also dependent on functional insulin receptor (IR) and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) receptor (IGF1R) signaling. Previous studies addressed this issue and reported a correlation between high insulin
-
The advantage of active immunotherapy
2024-09-05
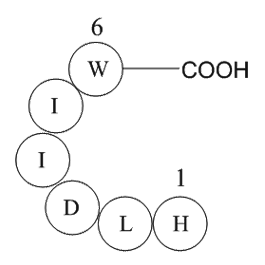
The advantage of active immunotherapy is long-term antibody production from short-term drug administration at limited cost. Conversely, immune response may be inconsistent or lacking, especially in older individuals, and adverse reactions—if immunologically based—may also be long-lasting. Initial ex
-
br Acknowledgments and Disclosures br Introduction Over the
2024-09-05
Acknowledgments and Disclosures Introduction Over the last decade, the most visible strategy for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD) has been amyloid β peptide (Aβ) immunotherapy (reviewed in [1]). Although the first efforts with Aβ immunotherapy failed to complete clinical trials [1], A
-
Aberrant lipid levels are associated
2024-09-05
Aberrant lipid levels are associated with various disorders, including vascular diseases and diabetes. Furthermore, important events support the idea that lipids, especially cholesterol and its derivatives, have a fundamental role in the physiopathology of AD. The Nifuroxazide is rich in cholestero
-
br Acknowledgments This work was supported by Grant
2024-09-05
Acknowledgments This work was supported by Grant-in-aid for Scientific Research (S) (20229008) (to T.K.), Targeted Proteins Research Program (to T.K.), the Global COE Research Program (to T.K.) and Translational Systems Biology and Medicine Initiative (to T.K.) from the Ministry of Education, Cul
-
Because of its role in tumor growth
2024-09-04
Because of its role in tumor growth, proliferation and metastasis, Axl is considered a therapeutic target. Several Axl inhibitors, including low-molecular-weight agents and antibodies, have been reported. Axl inhibition, using low-molecular-weight inhibitors or shRNA knockdown, resulted in reduced t
-
Chromatin proteins play important roles
2024-09-04
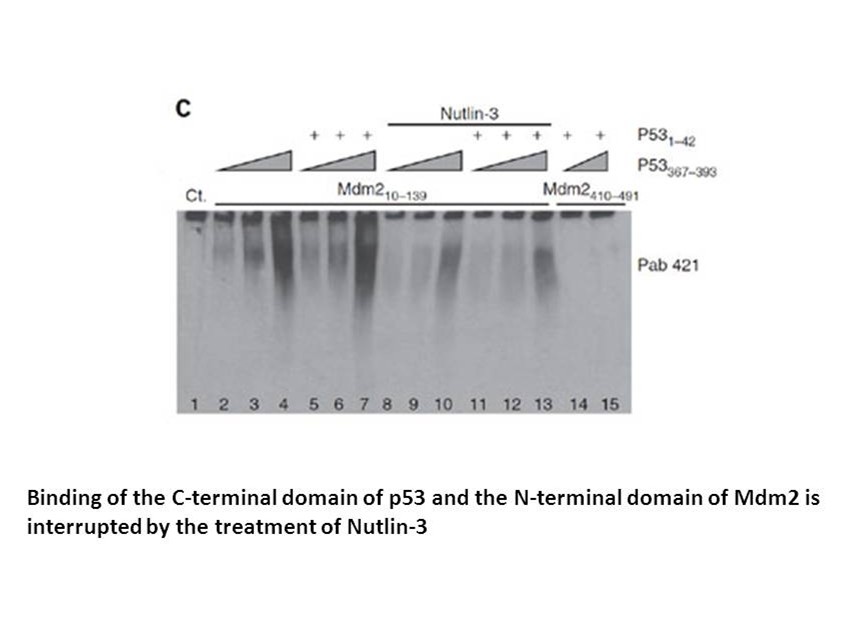
Chromatin proteins play important roles in gene expression and DNA repair. The importance of chromatin composition on gene expression is exemplified by X-inactivation, where one of the two X chromosomes in female mammalian hydroxycarboxylic acid receptors is transcriptionally silenced by heterochro
-
The canonical binding sites to
2024-09-04
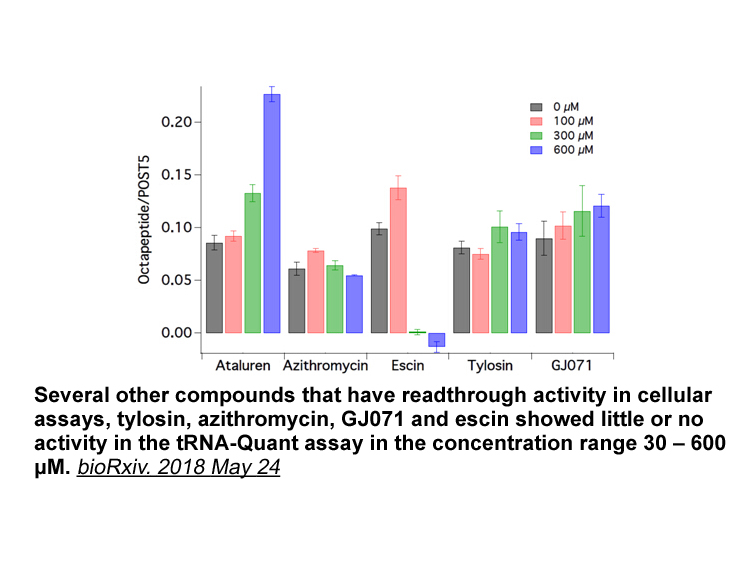
The canonical rna helicase to which α2, α3, or α5 contribute are highly similar. Therefore, differences in ligand affinity will not be large even if a ligand makes optimal use of the small differences in the pockets. As a possible alternative approach to achieve separation of compound effects, ligan
-
Crystal structures were obtained of sulfonamide and amide
2024-09-04
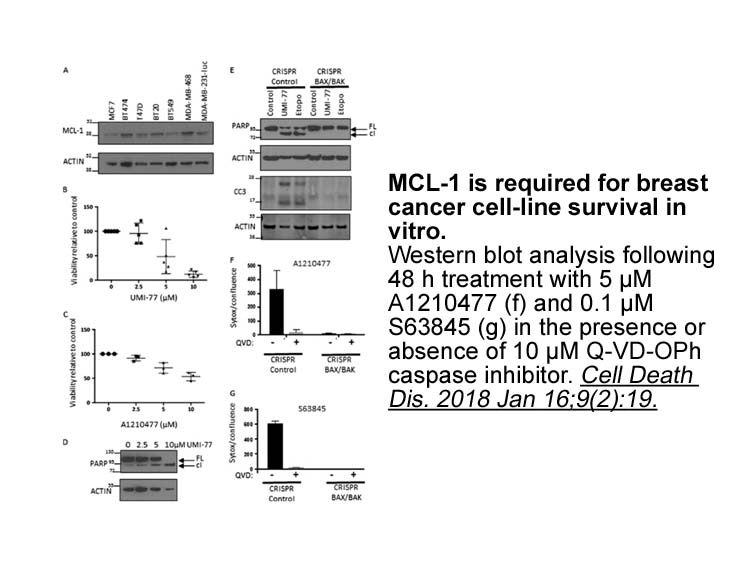
Crystal structures were obtained of sulfonamide 18 and amide 19 as a derivative of amide 36 (Fig. 7A and B). The precise rotameric orientation of amide 36 was of significant interest to understand the compound's interaction with the protein. As it would be difficult to assign the rotomer of 36, the
-
Lubiprostone mg br Author Contributions br Acknowledgments b
2024-09-04
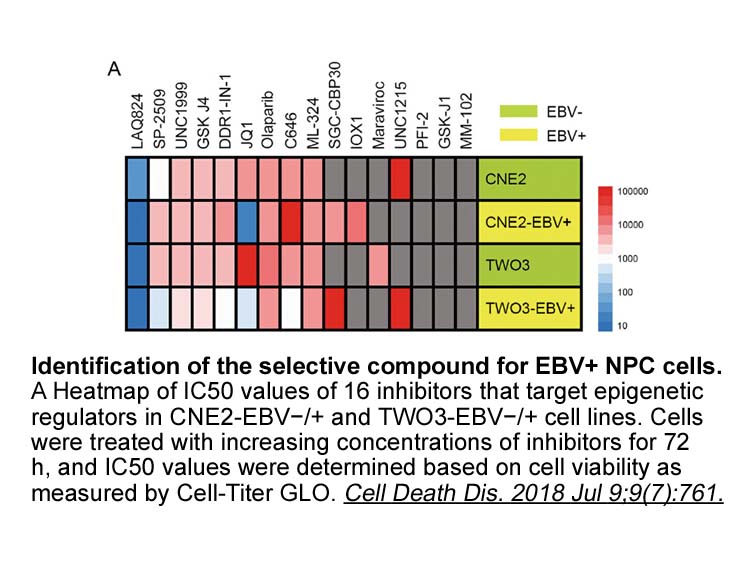
Author Contributions Acknowledgments Introduction Cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury is a pathological phenomenon that occurs after restoration of blood supply to Lubiprostone mg tissues subsequent to ischemia or hypoxia (Carden and Granger, 2000). It typically occurs after therape
-
The PAS domains of AHR consist of two regions
2024-09-03
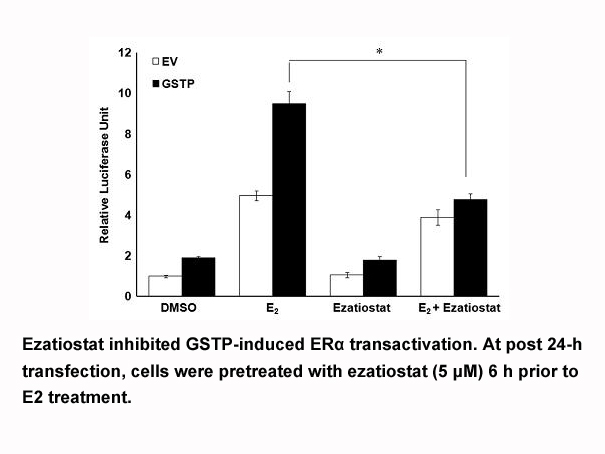
The PAS domains of AHR consist of two regions, PAS-A and PAS-B, which function as interfaces for dimerization with ARNT and for ligand binding, respectively [14]. Although both the bHLH and the PAS-A domains have been shown to be involved in dimerization with ARNT, a recent report suggests that only
-
In the search for more
2024-09-03
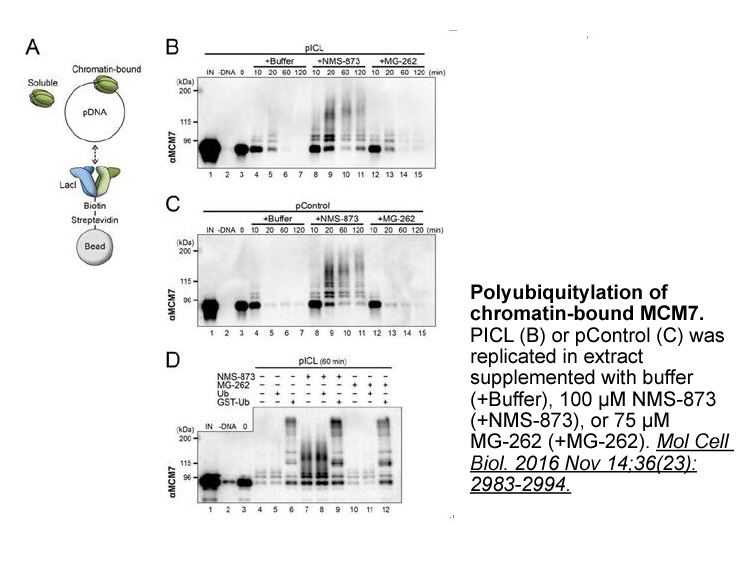
In the search for more specific inhibitors of uptake2, Iversen and Salt (1970) speculated that steroids may potentiate the actions of catecholamines on vascular smooth muscle by inhibiting uptake2-mediated catecholamine clearance of the transmitters. They went on to demonstrate that a variety of ste
-
We also demonstrate that PACAP
2024-09-03

We also demonstrate that PACAP treatment dose-dependently disrupts performance in the 5CSRTT, suggestive of attentional deficits, another core feature of mood and anxiety disorders. Treatment with PACAP (.5–1.0 µg) decreased the percentage of correct responses, increased the percentage of trials in
14368 records 100/958 page Previous Next First page 上5页 96979899100 下5页 Last page